This exercise is our introductory exercise in strength theory and deals with the following questions:
- How to calculate the normal force in a member?
- How to establish an equilibrium of forces with internal forces?
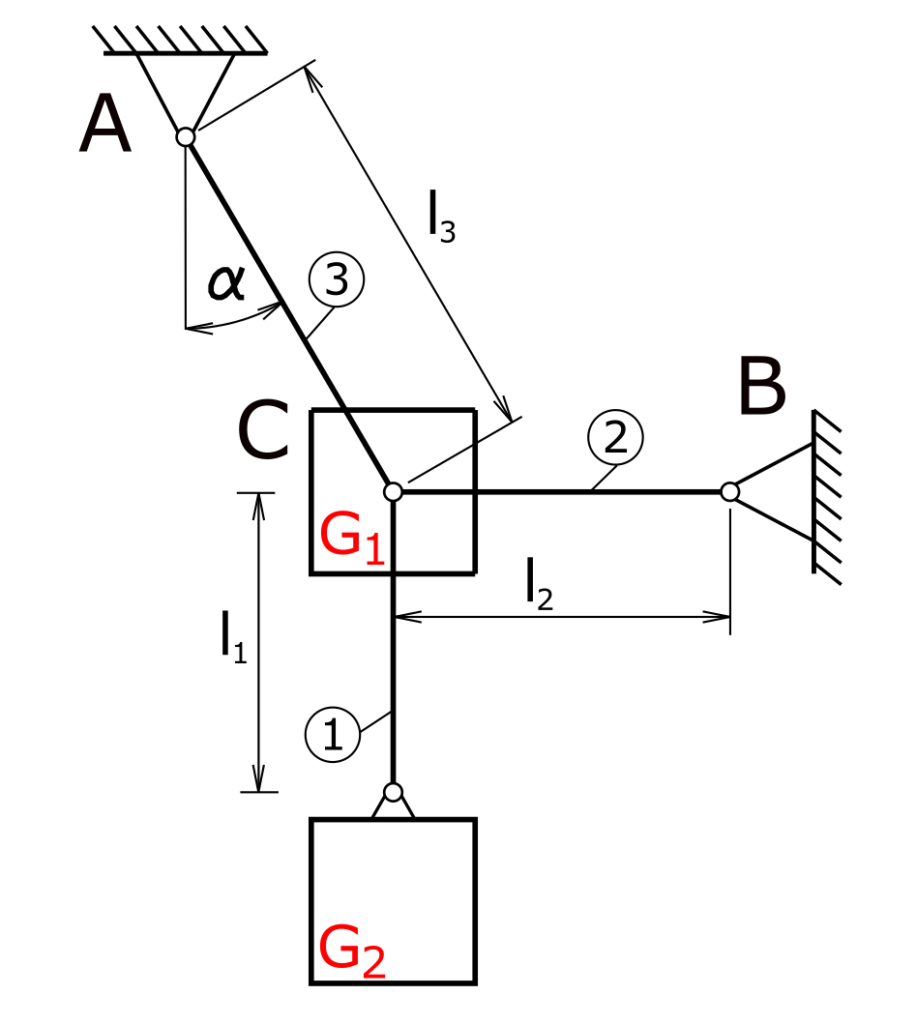
Task
A weight G2 is attached to a rod. The weight G1 is applied at connection point C. The members 1 and 2 are fastened with fixed bearings. The members are without mass.
The normal forces that occur in members 1 to 3 have to be calculated.
Solution
The normal forces are referred to as N and the index of their member number. The normal force in member 1 is the easiest to calculate.
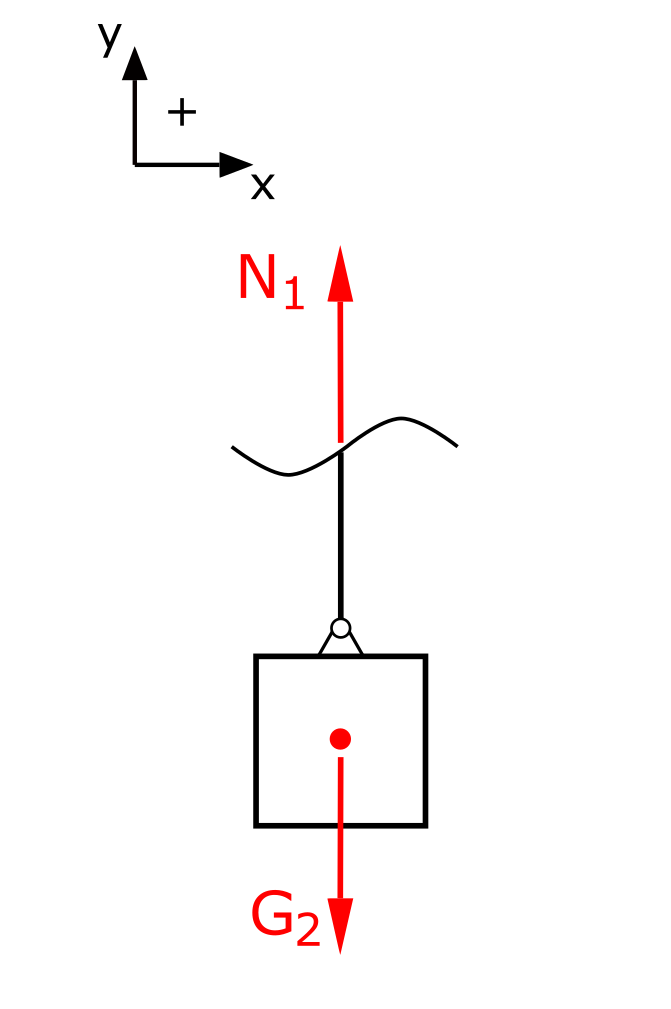
The equilibrium of forces in the y-direction yields
\[ \tag{1} \sum F_y = 0 = N_1 - G_2\]
\[ \tag{2} N_1 = G_2\]
Now, starting from point C, mentally cut through the members and apply their respective normal forces. A small trap lurks here in this task, because the force G1 must of course not be missing in this free cut.
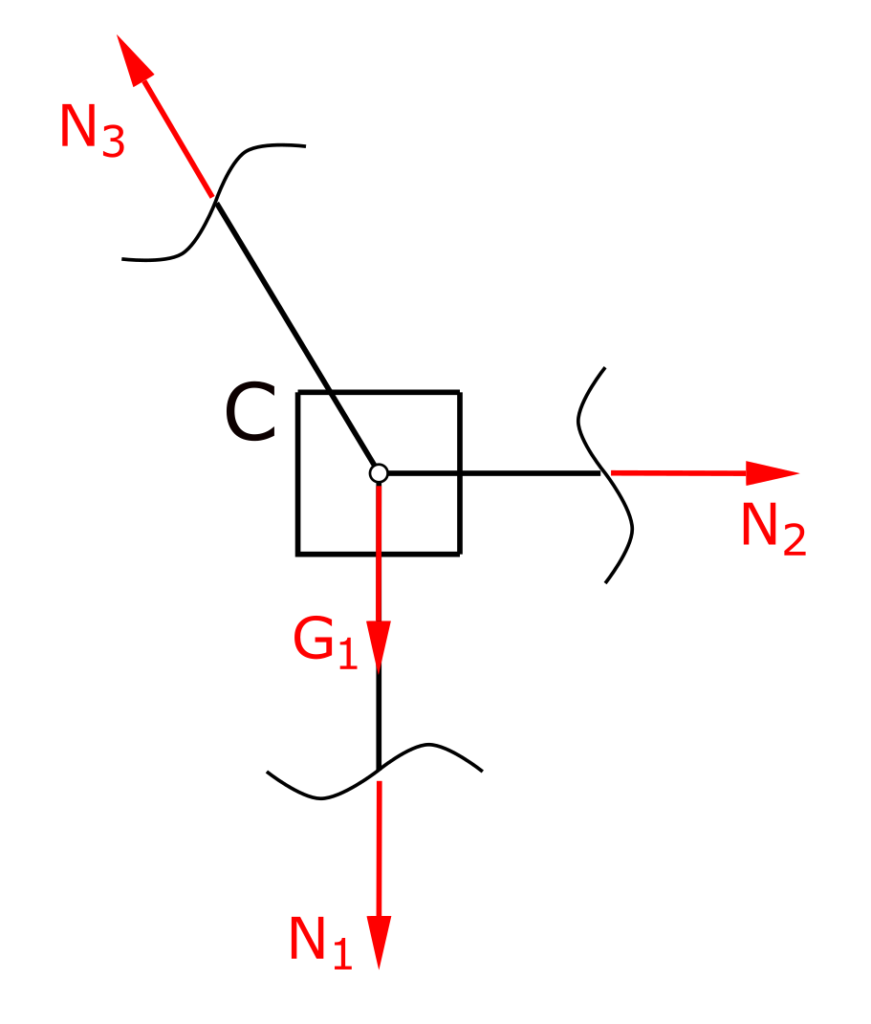
The two normal forces in members 2 and 3 can now be calculated using the force equilibria in the x and y directions.
\[ \tag{3} \sum F_x = 0 = - N_3 \cdot sin \alpha + N_2\]
\[ \tag{4} \sum F_y = 0 = N_3 \cdot cos \alpha - G_1 - N_1\]
or converted to N3 and the normal force N1 replaced by its value:
\[ \tag{5} N_3 = \frac{G_1 + G_2}{cos \alpha} \]
Finally, N2 follows from equation 3
\[ \tag{6} N_2 = \frac{G_1 + G_2}{cos \alpha} \cdot sin \alpha\]
or in other words:
\[ \tag{7} N_2 = (G_1+G_2) \cdot tan \alpha\]
The member lengths given in the sketch were not relevant for the calculation of the normal forces.

